- Home
- »
- Automotive & Transportation
- »
-
Robotaxi Market Size And Share, Industry Report, 2030GVR Report cover
![Robotaxi Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Robotaxi Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Propulsion Type, By Component Type, By Level Of Autonomy, By Vehicle Type, By Service Type, By Application, By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2025 - 2030
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-615-5
- Number of Report Pages: 130
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Technology
Robotaxi Market Summary
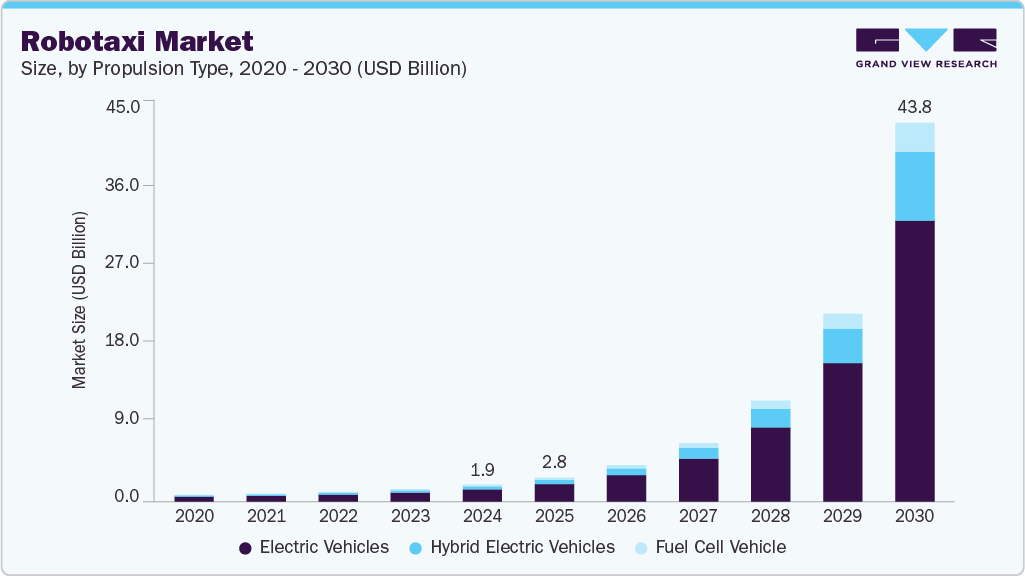
The global robotaxi market size was estimated at USD 1.95 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 43.76 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 73.5% from 2025 to 2030. The growth of the robotaxi industry is driven by significant advancements in autonomous vehicle (AV) technology, especially regarding the development of Level 4 and Level 5 automation systems.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- The Asia Pacific robotaxi industry accounted for a 36.0% share of the overall market in 2024.
- By propulsion type, the electric vehicles segment represented the largest share at 72.2% in 2024.
- By component, the LiDAR segment held the largest share of the robotaxi industry in 2024.
- By level of autonomy, the Level 4 segment dominated the robotaxi market in 2024.
- By vehicle type, the cars segment dominated the robotaxi industry in 2024.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 1.95 Billion
- 2030 Projected Market Size: USD 43.76 Billion
- CAGR (2025-2030): 73.5%
- Asia Pacific: Largest market in 2024
Innovations in artificial intelligence, machine learning, computer vision, and real-time sensor fusion have allowed vehicles to perceive and respond to dynamic environments with increasing accuracy. Major players such as Waymo, Baidu, and Cruise are conducting extensive testing and limited commercial deployments, which validate the growing maturity of autonomous systems. These advancements are diminishing the need for human intervention, a key requirement for scalable robo-taxi services.The global shift toward shared mobility is driving the demand for robo-taxis as part of broader Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) frameworks. Consumers, particularly in urban areas, are moving away from traditional car ownership in favor of flexible, on-demand transportation options. Robo-taxis provide a seamless user experience that includes real-time vehicle booking, digital payments, and efficient routing. The convenience and cost-effectiveness of this model are especially attractive in congested cities where parking is limited and traffic is a daily concern. Moreover, robo-taxis can be integrated with public transportation networks to offer first-mile/last-mile connectivity, enhancing urban mobility systems. MaaS platforms that incorporate robo-taxis help reduce traffic volumes, lower emissions, and optimize transportation assets. As more cities implement digital mobility strategies, robo-taxis are expected to play a critical role in creating smarter, user-centric transportation networks.
Supportive regulatory frameworks and government-led pilot programs are key growth drivers for the robo-taxi market. Countries such as the U.S., China, Germany, and the UAE are actively fostering environments that support the testing and deployment of autonomous vehicles. Regulations regarding data sharing, safety protocols, and liability management are evolving to meet the unique needs of autonomous ride-hailing. For example, California and Arizona in the U.S. have been pioneers in allowing real-world testing and limited commercial operations of robo-taxis. Additionally, public-private partnerships are forming to develop smart infrastructure, including autonomous lanes, dedicated pickup zones, and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication systems. Government incentives and grants are further promoting innovation in autonomous mobility. Although regulatory challenges remain in many areas, progress is being made toward the global harmonization of standards.
Robo-taxis are increasingly being developed as electric vehicles (EVs), aligning with global goals for cleaner transportation and reduced carbon emissions. Electrification offers dual benefits for fleet operators-lower fuel and maintenance costs, as well as compliance with tightening emission regulations in urban areas. As cities implement low-emission zones and net-zero mobility targets, electric robo-taxis are emerging as ideal solutions for sustainable urban transit. Automakers and tech firms are designing battery-electric robo-taxi models optimized for range, ride comfort, and fleet operation. Companies like Tesla, Hyundai, and GM are aligning their autonomous strategies with EV production to create a future-proof transportation model. Moreover, government subsidies for EVs and investments in charging infrastructure are facilitating the deployment of electric robo-taxis. The synergy between autonomy and electrification not only enhances vehicle efficiency but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible mobility options.
Propulsion Type Insights
The electric vehicles segment represented the largest share at 72.2% in 2024. Electric vehicles (EVs) are the dominant propulsion type in the robotaxi Industry, driven by their alignment with global sustainability goals and the economic advantages they offer to fleet operators. EVs have significantly lowered operating costs due to reduced fuel and maintenance requirements, making them highly suitable for high-usage, autonomous ride-hailing applications.
Governments in key regions such as the U.S., China, and the EU are providing strong regulatory support in the form of tax incentives, emissions regulations, and investment in EV charging infrastructure. Technological advancements in battery performance, like increased range, faster charging, and longer lifecycle, have further enhanced the viability of electric robo-taxis for continuous urban operations. As cities strive for net-zero transportation systems and expand low-emission zones, EV-based robo-taxi fleets are becoming a central element of smart urban mobility strategies.
The hybrid electric vehicles segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are emerging as a viable transitional segment in the robotaxi market, particularly in regions where electric infrastructure is underdeveloped or longer travel ranges are necessary. HEVs combine internal combustion engines with electric propulsion, providing the flexibility to operate in areas lacking dense EV charging networks. This makes them particularly appealing for semi-urban or intercity robo-taxi services, where reliability and range are major concerns.
Moreover, HEVs enable fleet operators to begin transitioning toward greener mobility without fully relying on high-voltage charging infrastructure. As the adoption of autonomous vehicles expands beyond major metropolitan areas, HEVs offer a practical interim solution that bridges the gap between traditional fuel-based vehicles and fully electric fleets. Although not as environmentally optimal as EVs, the reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency of hybrids still positively contribute to sustainability goals.
Component Type Insights
The LiDAR segment held the largest share of the robotaxi market in 2024. LiDAR sensors provide robust depth perception and spatial awareness, making them critical for safe navigation in complex urban environments and an essential requirement for Level 4 and Level 5 autonomy. As autonomous driving systems evolve, the need for detailed environmental mapping and redundancy in sensor inputs is increasing, further solidifying LiDAR’s role as a core component in robo-taxi architectures. Leading companies are investing in cost reduction, miniaturization, and solid-state LiDAR to make these systems more commercially viable for fleet-wide deployment. Regulatory bodies also favor the inclusion of LiDAR in safety-critical applications, reinforcing its dominance. The reliability, accuracy, and evolving affordability of LiDAR systems establish them as a foundational technology in next-generation autonomous mobility.
The camera segment is projected to grow at a significant CAGR over the forecast period. Cameras provide high-resolution visual data that is crucial for tasks such as traffic sign recognition, lane detection, and pedestrian tracking, particularly in well-lit, structured environments. They are considerably more cost-effective than LiDAR, making them appealing to automakers looking to balance performance with affordability in mass-market robo-taxi deployments. Additionally, camera systems are becoming increasingly reliable when combined with AI-based perception algorithms that facilitate real-time decision-making. As sensor fusion gains traction, cameras are playing a complementary role alongside LiDAR and radar to establish a comprehensive situational awareness stack.
Level Of Autonomy Insights
The Level 4 segment dominated the robotaxi market in 2024. Vehicles operating at Level 4 can perform all driving tasks without human intervention in specific scenarios, such as mapped city centers, business districts, or dedicated shuttle routes. Companies like Waymo, Cruise, and Baidu Apollo are already piloting or commercially deploying Level 4 robo-taxi services in cities like Phoenix, San Francisco, and Beijing. Regulatory frameworks and public acceptance are more favorable toward Level 4 deployments due to their confined operational design domains (ODDs), which help mitigate safety and liability concerns. The controlled nature of Level 4 environments allows for more predictable system performance, making it the most practical and scalable model for near-term robo-taxi growth.
The Level 5 segment is expected to exhibit the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Level 5 autonomy represents the ultimate goal of the robo-taxi market, characterized by full automation without the need for steering wheels, pedals, or human oversight, and capable of operating under all conditions and environments. While it remains in the emerging stage, Level 5 is attracting significant interest as technological innovations in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and real-time environmental perception continue to accelerate.
Companies are investing in long-term R&D to address the remaining challenges, such as complex edge-case scenarios, unpredictable weather conditions, and regulatory standardization across regions. The appeal of Level 5 lies in its promise of complete flexibility, offering truly driverless mobility that can operate 24/7 in any location. While widespread deployment is not imminent, advancements in simulation, testing protocols, and global collaboration between tech companies and policymakers are gradually paving the way for Level 5 robo-taxis.
Vehicle Type Insights
The cars segment dominated the robotaxi market in 2024. Autonomous passenger cars are well-suited for urban ride-hailing services, where compact design and easy maneuverability are essential for navigating dense city environments. Their smaller size makes them ideal for curbside pickups, tight turns, and navigating existing road networks without requiring significant urban planning changes. Leading robo-taxi companies like Waymo, Cruise, and Zoox have primarily focused on car-based models for their pilot programs and early commercial operations. The familiarity of car designs also promotes higher user acceptance and regulatory approval. Additionally, cars are generally more energy-efficient per trip and simpler to service and maintain than larger vehicles.
The shuttles/vans segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Shuttles and vans are emerging as a promising segment in the robo-taxi market, particularly for high-capacity and shared mobility use cases. These vehicles are gaining traction for transporting multiple passengers efficiently across short to medium distances, such as within university campuses, airport terminals, corporate parks, and urban transit hubs. With their larger interior space and modular seating configurations, shuttles and vans can accommodate group travel and offer better per-passenger economics for fleet operators. They are especially relevant in scenarios where transportation demand is predictable and route-based, making them ideal for first-mile/last-mile connectivity. As cities invest in smart mobility infrastructure and promote sustainable public transportation, autonomous shuttles are expected to play an increasingly important role.
Service Type Insights
The car rental segment dominated the robotaxi market in 2024 and is projected to grow at a significant CAGR over the forecast period. The car rental segment dominates the robo-taxi service landscape, primarily driven by its convenience, flexibility, and alignment with current ride-hailing models. Users prefer on-demand mobility services that enable them to summon autonomous vehicles directly to their location via mobile apps, mimicking traditional ride-share experiences. This door-to-door approach minimizes wait times and offers seamless point-to-point connectivity, making it ideal for urban commuters and business travelers. Key players like Waymo and Cruise have embraced this model in their pilot and commercial deployments, concentrating on dynamic fleet distribution based on real-time demand. Furthermore, the car rental model facilitates scalable operations, flexible pricing, and improved fleet utilization.
The station-based segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. The station-based segment is emerging as a structured alternative to traditional car rental-style robo-taxi services, particularly in planned urban developments, smart campuses, and transport-integrated city zones. In this model, autonomous vehicles operate between fixed pickup and drop-off stations, offering predictable routes, lower logistical complexity, and easier integration with existing public transport systems. Station-based robo-taxis are well-suited for repetitive, high-volume routes such as airport shuttles, business districts, and residential communities. This approach also eases regulatory concerns, as operations are limited to pre-approved routes and zones. While it lacks the flexibility of the car rental model, it offers benefits in terms of operational control, cost management, and safety monitoring.
Application Insights
The passenger segment held the largest market share in 2024. The passenger segment dominates the robotaxi industry, driven by increasing demand for on-demand urban mobility and the growth of autonomous ride-hailing services in major cities. Robo-taxis are primarily designed to offer convenient, safe, and cost-effective transportation for individuals and groups, particularly in congested urban areas where traditional car ownership is declining.
Companies such as Waymo, Baidu, and Cruise have concentrated their initial deployments on passenger mobility, providing user-friendly ride-booking apps and seamless door-to-door transport. The scalability, reduced cost per ride, and elimination of human drivers enhance the appeal of robo-taxis for everyday commuting, airport transfers, and city travel. Furthermore, the increasing emphasis on smart cities and sustainable transport infrastructure continues to facilitate the rollout of autonomous passenger vehicles as part of broader urban mobility strategies.

The goods segment is projected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. The goods segment is emerging as a promising application, fueled by the growing demand for last-mile delivery solutions and the e-commerce surge. Autonomous vehicles designed for goods transport are being tested and deployed to deliver parcels, groceries, and small cargo in urban and suburban areas with high efficiency. The goods application enjoys fewer regulatory hurdles compared to passenger transport, as safety standards for unmanned cargo deliveries are typically less stringent. Retailers and logistics companies are collaborating with tech firms to pilot autonomous delivery pods and small robo-vans, seeking to shorten delivery times and cut costs. This segment is particularly attractive in regions with high population density and frequent delivery needs, where automation can enhance operations and diminish reliance on human labor.
Regional Insights
The North America robotaxi market was identified as a lucrative region in 2024. The region leads due to advanced autonomous vehicle regulations, strong R&D investment, and a growing push toward sustainable urban mobility. The U.S. remains at the forefront with companies like Waymo, Cruise, and Zoox conducting large-scale testing and pilot operations. Federal and state-level legislation is becoming increasingly favorable, encouraging commercial deployments in select urban zones.
U.S. Robotaxi Market Trends
The U.S. robotaxi market held a dominant position in 2024. The country’s leadership is underscored by the early adoption of AV-friendly policies and a significant influx of venture capital into autonomous mobility startups. Cities like San Francisco, Phoenix, and Austin are functioning as live testbeds for Level 4 autonomous ride-hailing services. In 2024, Cruise expanded its commercial operations to include daytime hours, while Waymo increased its fleet size to meet rising demand. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Department of Transportation (DOT) continue to refine regulatory frameworks, promoting vehicle safety standards while streamlining AV testing approvals.
Europe Robotaxi Market Trends
The Europe robotaxi Industry was identified as a lucrative region in 2024. The Europe market is gaining traction, especially in countries with strong urban mobility programs and emission reduction targets. The EU’s Green Deal and Smart Mobility Strategy support autonomous transport as a way to decarbonize cities. Germany and France are leading in pilot initiatives for autonomous ride-hailing, with OEMs like BMW, Volkswagen, and Renault investing in in-house robo-taxi platforms or partnerships.
The robotaxi market in the U.K. has witnessed rapid growth with support from the Centre for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CCAV) and real-world testing in cities such as Milton Keynes and London. British firms like Oxbotica are advancing software platforms for driverless urban taxis, while AV trials in Cambridge are linking university campuses with transit hubs using electric autonomous shuttles.
Asia Pacific Robotaxi Market Trends
The Asia Pacific robotaxi market accounted for a 36.0% share of the overall market in 2024. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are leading the way, while others like Singapore and Australia invest in pilot programs to evaluate scalability. The region's densely populated urban areas and increasing demand for sustainable mobility solutions create a fertile environment for autonomous ride-hailing services. Key factors, including 5G integration, smart city initiatives, and AI-based fleet optimization, are speeding up adoption. However, regulatory harmonization, infrastructure readiness, and public acceptance remain critical to large-scale deployment across the broader region.

The robotaxi market in China is growing at a rapid pace. The country’s densely populated urban areas and increasing demand for sustainable mobility solutions create a fertile environment for autonomous ride-hailing services. Key factors like 5G integration, smart city initiatives, and AI-based fleet optimization are speeding up adoption. However, regulatory harmonization, infrastructure readiness, and public acceptance remain crucial for mass-scale deployment across the broader region.
The Japan robotaxi market is expected to grow over the forecast period. Japan is steadily advancing its robo-taxi ecosystem as part of its broader Society 5.0 vision, which incorporates robotics, AI, and digital infrastructure into everyday life. The country is tackling key social challenges, such as an aging population and the urban-rural divide, through autonomous mobility. Government-backed trials are currently underway in regions like Fukushima, Hokkaido, and Tokyo, focusing on use cases ranging from autonomous shuttles in smart cities to teleoperated taxis in remote areas. Companies such as Toyota, SoftBank, and DeNA are leading efforts in autonomous vehicle development, including deploying the e-Palette platform.
Key Robotaxi Company Insights
Some of the major players in the robotaxi market include Waymo LLC, Baidu, Inc.; Beijing Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Ltd.; Cruise LLC; and EasyMile. These companies are at the forefront of deploying autonomous vehicle technologies, enabling safe, efficient, and intelligent urban mobility solutions that are crucial for the future of transportation. Their significant investments in R&D, strategic collaborations with automotive OEMs, AI developers, and city planners, along with extensive real-world testing, have positioned them as key enablers of the robo-taxi ecosystem.
-
Waymo LLC, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., is widely recognized as a pioneer in the autonomous vehicle and robo-taxi industry. With its flagship service, Waymo One, the company operates fully driverless robo-taxis in multiple U.S. cities, including Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Austin. Leveraging advanced sensor technologies, AI-powered driving systems, and millions of autonomous miles logged, Waymo has established itself as one of the most mature and commercially viable players in the market. The company’s focus on safety, scalability, and user experience has enabled it to lead the development of autonomous urban mobility, setting benchmarks for the industry worldwide.
-
Baidu, Inc. is one of the prominent companies in China’s autonomous driving space through its Apollo Go robo-taxi platform. Supported by strong government backing and strategic investments, Baidu has deployed hundreds of fully autonomous vehicles across major Chinese cities such as Wuhan, Beijing, and Chongqing. Apollo Go integrates cutting-edge AI, deep learning, and sensor fusion technologies to deliver reliable driverless rides in complex urban environments. Baidu’s extensive focus on collaboration with local governments and infrastructure providers has accelerated the adoption of robo-taxi services in China, positioning the company as a dominant player driving the future of smart, connected mobility in the region.
Key Robotaxi Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the robotaxi market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Waymo LLC
- Baidu, Inc.
- Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Ltd.
- Cruise LLC
- EasyMile
- Tesla Inc.
- Aptiv
- Uber Technologies Inc.
- Lyft, Inc.
- Zoox, Inc.
Recent Developments
-
In May 2025, Tesla, Inc. announced it would begin testing its long-anticipated robotaxi service in Austin, Texas, by the end of June. The initial rollout will include around 10 self-driving vehicles operating in select areas of the city. Over the following months, the company plans to scale the fleet up to approximately 1,000 vehicles. This move comes as Tesla continues to push forward with its autonomous vehicle ambitions. However, the launch coincides with ongoing safety scrutiny from a U.S. regulatory body.
-
In July 2024, Waymo LLC secured a USD 5 billion multi-year investment announced during Alphabet’s Q2 2024 earnings call. The funding supported Waymo’s expansion, which had already completed over 2 million trips and accumulated more than 20 million fully autonomous miles. By mid-2024, Waymo was delivering over 50,000 weekly paid rides in cities like San Francisco and Phoenix, and began offering commercial services in Los Angeles while preparing to launch in Austin. The company surged ahead in the robo-taxi market after rival Cruise suffered a major setback due to a pedestrian injury incident in San Francisco, leading to license suspensions and project cancellations. As Cruise struggled with fallout, including GM canceling its Origin robo-taxi, Waymo solidified its leadership in the autonomous mobility space.
Robotaxi Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 2.79 billion
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 43.76 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 73.5% from 2025 to 2030
Base year for estimation
2024
Historical data
2018 - 2023
Forecast period
2025 - 2030
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million/billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2030
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Propulsion type, component type, level of autonomy, vehicle type, service type, application, and region
Regional scope
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; Germany; UK; France; China; Japan; India; South Korea; Australia; Brazil; KSA; UAE; South Africa
Key companies profiled
Waymo LLC; Baidu, Inc.; Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Ltd.; Cruise LLC; EasyMile; Tesla Inc.; Aptiv; Uber Technologies Inc.; Lyft, Inc.; Zoox, Inc.
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Global Robotaxi Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at the global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global robotaxi market report based on propulsion type, component type, level of autonomy, vehicle type,service type, application, and region.
-
Propulsion Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Electric Vehicles
-
Hybrid Electric Vehicles
-
Fuel Cell Vehicle
-
-
Component Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
LiDAR
-
Radar
-
Camera
-
Sensor
-
-
Level of Autonomy Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Level 4
-
Level 5
-
-
Vehicle Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Cars
-
Shuttles/Vans
-
-
Service Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Car Rental
-
Station-based
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Passenger
-
Goods
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
France
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
Japan
-
India
-
South Korea
-
Australia
-
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
-
Middle East and Africa (MEA)
-
KSA
-
UAE
-
South Africa
-
-
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We offer custom report options, including stand-alone sections and country-level data. Special pricing is available for start-ups and universities.
Request Customization![Certified Icon]()
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."





